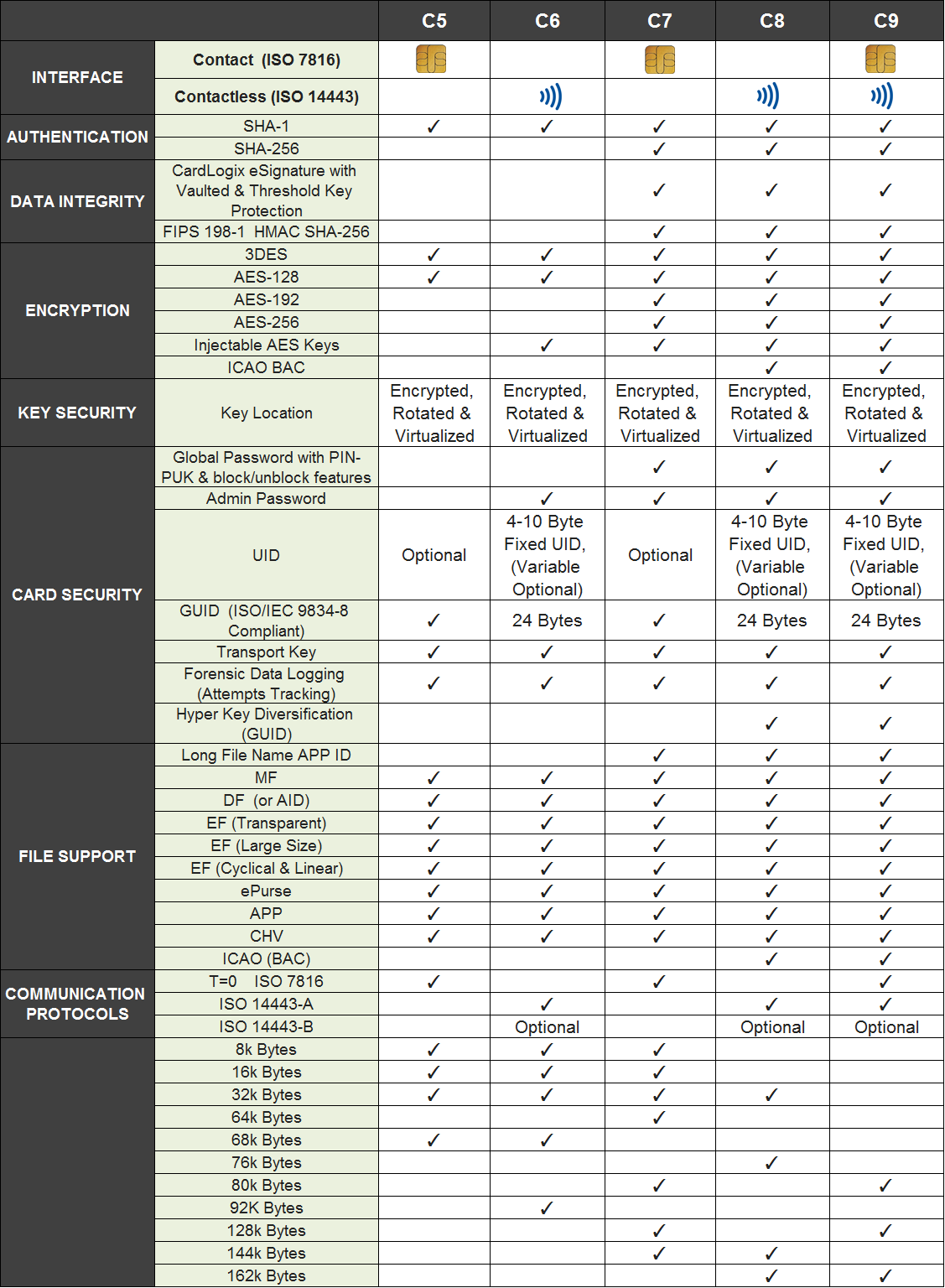
Features
Smart Alternative to MIFARE, ProxCard and iClass Cards
The M.O.S.T. Card C6 gives you a robust contactless (RFID) interface backed by an intelligent operating system and microprocessor with more available user memory, more advanced encryption algorithms, and more security features than a MIFARE, ProxCard (Proximity cards), or iClass card—all at a lower cost to the end user. The M.O.S.T. Card C6 leverages the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) for data encryption, the strongest encryption algorithm to date, so that your data will remain 100% confidential no matter where it is transmitted. AES has typically been found on card operating systems that support public key infrastructure, but now users can get PKI security at the price of a contactless symmetric key card.
High Security Architecture — Powered by the M.O.S.T. Card® Operating System
The M.O.S.T. Card C6 is powered by CardLogix’ proprietary M.O.S.T Card Operating System which supports a variety of security measures, including SHA-1 bi-directional / mutual authentication, AES, DES, and 3DES, PIN/passwords, and internal random number generation for unique e-signatures and transaction sessions. The OS is built with an error detection code and security self-tests. The EAL certified silicon provides continuous encryption of all data and the virtualization of the data across the non-volatile memory.
Large EEPROM Storage Capacity — Up to 68k Bytes
The M.O.S.T. Card C6 family offers up to 68k bytes of user memory. The large storage capacity increases the card and password functionality, enabling multiple applications on one card, and substantially increasing security. The C6 family allows a user to safely store and transmit a large amount of personal and sensitive data contactlessly, including biometric information —data too vulnerable to manage over a loosely protected network. The M.O.S.T. Card C6 is capable of managing card holders’ and card issuers’ data on the card so that physical access controls systems, loyalty, e-payment and in-the-field civil ID, national ID and military identification programs can benefit from a secure closed system that does not rely on being connected to a network at all times.
Multiple Applications On One Card for Better Cost-Efficiency
With the M.O.S.T. Card C6, your organization can benefit from the economies of scale achieved by using one card for multiple purposes. Why settle for a single-purpose memory card like the iClass or ProxCard when a company can combine a physical access control system (PACS), customer loyalty program, multi-factor identification, e-payment system, single sing on, and player/ customer tracking onto one company-branded M.O.S.T. Card for the same price or less as a memory card? Improve your organization’s security by arming your employees with the M.O.S.T. Card to handle multi-factor authentication and non-refutable identification. Use the same card to control facility access rights, to institute an employee incentive program, and to protect classified or sensitive data. The application possibilities are endless, and the M.O.S.T. Card C6 can handle it all to meet any of your organization’s needs.
Admin Password & Injectable AES Keys — Ideal for PACS System Management
During the design phase of the M.O.S.T. Card C6, using M.O.S.T. Toolz™ Card Configuration Utility, the card issuer creates an Administration Password File, protected by a password that cannot be accessed or changed after construction. With the Admin Password File, an authorized security systems control manager can add injectable AES Keys should door locks be changed or should any password modifications be needed. This allows the manager the flexibility to safely update his or her physical access control system without having to re-issue cards.
Rapid Smart Card System Development for Flexible and Easy-to-Build Card Applications
CardLogix has provided a complete line of user-friendly development tools to create both custom and pre-configured smart card applications. Project development for the M.O.S.T. Card C6 is supported by the PCSC API and the M.O.S.T. Toolz™ Card File Creation Utility SDK, including the powerful Winplex® API. The M.O.S.T. Toolz File Creation Utility features an intuitive user-interface that allows a card issuer the flexibility to design a M.O.S.T. Card file structure and set passwords that fit the needs of any custom smart card program. M.O.S.T. Toolz also provides intelligently constructed, pre-configured idblox™ applications cards, leveraging the M.O.S.T. Card Operating System. With this option, a card issuer’s only job is to setup passwords. Smart card development could not get any easier.
Eliminate the need to hire a graphic designer by starting with one of CardLogix’ professionally designed, pre-printed ReadyStart™ Secure Cards or Holofoil Cards, with embedded 2D holograms. Both use high security graphic printing technology that provides additional levels of physical security to your M.O.S.T. Card®
True Software and Hardware Interoperability — idblox™ Compatible
The M.O.S.T. Card C6 family is future-proofed, working on multiple silicon vendors’ devices so that your projects are always supported. The card family is part of the idblox™ ecosystem which has attracted multiple vendors for compatible smart card readers, smart card terminals, smart card applications and all other smart card infrastructure components. The idblox ecosystem leverages a unique methodology that enables true card system interoperability without requiring programming.
Learn more about the idblox™ ecosystem, the only smart card ecosystem with true interoperability that enables the fastest, easiest and most affordable creation of high-security smart card programs for any card application.
Smart Card Personalization Made Easy — The Card Encoding Engine™
The M.O.S.T. Card family is supported by the latest innovation in smart card personalization — The Card Encoding Engine™. The Card Encoding Engine is the first of its kind to offer smart card encoding without requiring programming first in order to do so. This revolutionary software engine is the cornerstone of idblox, allowing inline creation of a smart eID card program from design to use without relying on programmers.
Seamless Biometric Enrollment and Card Issuance of Biometric Smart Cards
CardLogix is strategically partnered with Corvus Integration, Inc., experts in biometric enrollment and biometric verification technologies, to bring you the simplest way to register personnel’s biometric information and load it onto a smart card within minutes. Biometric data combined with a smart card provides the highest security and protection of personnel, data and valuable assets. With the M.O.S.T. Card C6, your organization can benefit from this level of security without having to spend more money than it’s worth.
Options
M.O.S.T. Card C6 Microprocessor Smart Cards are available in the following sizes:
- CLXSU064KC6/T=CLED (8k Bytes)
- CLXSU128KC6/T=CLED (16k Bytes)
- CLXSU256KC6/T=CLED (32k Bytes)
- CLXSU544KC6/T=CLED (68k Bytes)
- CLXSU736KC6/T=CLED (92k Bytes)
CardLogix Smart Cards are versatile and custom-made to meet Your Unique Requirements.
CardLogix is a full-service card manufacturer. Cards are built from the inside-out, from card substrate selection and artwork preparation to chip initialization, personalization, and many other card options.
For a comprehensive list of our card offerings, see the CardLogix Smart Card Product Selection Guide
Custom Card Options
CardLogix can build the card that’s right for your application(s). Card options include a variety of card technologies, security graphics, custom design and printing services, and card substrates. All CardLogix cards can be developed as hybrid cards with both a contact and contactless interface. They can be combined with additional card technologies such as CPU or memory chips, magnetic stripes, 1D/2D barcodes, and MRZs (Machine Readable Zones). Combination cards and hybrid cards expand application possibilities for an infinite number of ID card solutions. This versatility also enables the integration of newer card technologies into legacy readers and systems to protect existing technology investment and lifespan.
Card Technologies
Hybrid Cards – Combination Cards
Add a memory chip or UHF chip/ tag to your smart card for legacy applications, such as payments for catering, vending machines, parking, or transportation; or for physical access systems. CardLogix can provide many chip options, including HID Prox® and 1125mhz proximity. These chips use RFID, NFC, and UHF technologies that follow the ISO/IEC 14443, ISO 15693, and ISO 18092 standards. Add a contact chip card, such as one of CardLogix M.O.S.T. Card® C5 or C7 microprocessor chips, for applications that require a secure contact interface. Combine with a M.O.S.T. Card C6 or C8 microprocessor chip for highest-security, high-speed, contactless applications.
Magnetic Stripe
CardLogix offers a full lineup of magnetic stripe card (magstripe) options. Magnetic Stripes are a useful feature to add to your cards so that they continue to work with existing legacy card readers and software programs. Magstripes are a good option for Loyalty Card programs or Gift Card programs. CardLogix can pre-load custom data on the magnetic stripe or it can be customer-encoded. The magnetic stripe card works in conjunction with the promoter’s software in order to provide the cardholder with special offers, credit toward purchases, and marketing incentives. It s also used in building databases that help analyze buying habits of customers. This information is useful because retailers can better serve their customer base by stocking the products they are most interested in buying. It also has many more uses that offer a wealth of valuable marketing applications.
Magnetic stripe options:
- 2trk & 3trk
- LoCo (300oe), MidCo (2750oe), or HiCo (4000oe)
- Stripe and card color options: black, white, gold, silver, red, brown, blue, green, and holographic
Barcode
CardLogix can print sequential or custom numbered barcodes using barcodes such as 2D, PDF417, 3 of 9, HIBC, code 128, etc. Barcoding is a popular option that can be added to any card. Most modern retail cash register systems read barcodes at the checkout stand so this is the perfect and fastest way to gather information about customers and to see what they are buying. It is also a great way to manage memberships in facilities and operations that have many cards to flow in and out. Each card is capable of carrying a unique barcode on either the front or reverse side. Another advantage of an ID card with a barcode printed on it is that it can be scanned extremely quickly to identify the user.
Primary Card Artwork: Design & Printing
The same background artwork that you see on every card for a specific program? That’s the primary card artwork. The background artwork gets printed and embedded at the point of card manufacturing. As card layers are stacked together, so is your artwork.
CardLogix offers graphic design, artwork preparation, and consulting services for your primary card artwork. Send what you have, and we’ll do the rest.
Secondary Card Printing
This is what gets printed after your cards are in their final shape. Secondary printing usually involves variable data; that is, data that is different on each card. This includes serial numbers, photo IDs, cardholder data, and more.
Depending on the size of your project, CardLogix can do this for you. Services include printing unique ID card numbers to each card, serialized laser engraving, and more. For smaller runs or for applications that involve distributed, instant card issuance, we recommend purchasing one or more ID Card Printers with ID Card Printer Software, such as CardLogix’ Card Encoding Engine
Custom Security Graphics
Security graphics are usually applied to cards at the point of manufacture. They use very specific, high-end printing and engraving technologies that make cloning and fraud extremely difficult for perpetrators.
Signature panel
Customers have the option of including a signature panel on the reverse of the card or a digitally scanned signature on the front of the card. Adding a signature panel to your card gives makes it possible to add information on the card at a later time.
Embossing and Tipping
Tipping refers to coloring tip of the raised or embossed letters with certain colors to make the numbers or letters stand out from the card. Gold and silver colors are available.
Sequential Numbering
This option can be added to any card order to help in the identification of a card holder or special program that the number may be referencing.
Laser Engraving
Add your company logo or symbol to your card to increase security or brand awareness. You can also laser engrave a unique or sequential number and/or barcode.
Additional Graphic Options:
- Full color offset printing
- Silk-screen printing
- Silver/Gold silk-screen printing background
- Variable Data Printing, such as numbers, photos, PIN codes and other information that is unique to each card
- Sequential Numbering
Additional Security Options:
- Laser engraving/indenting
- Guilloche and rosettes
- Microprinting
- Optically Variable Devices (OVDs) and holograms
- Hidden Card Validator™ graphics with lens viewer
- Ultraviolet (UV) ink
- Watermark
- SBumps
- Holographic lamination
Other Security Graphics Options:
- Numbering: Jet dot/ Thermal transfer/ Laser engrave
- Many flood colors are available
- Scratch Off Panels that reveal unique ID’s such as PIN number
- Variety of card thickness
- Plain and custom (such as company logo) Tyvek card sleeves
- Card wallet book such as for passports and themed books for promotional purposes
- Hole punch for ID clip necklaces
- SIM punch and key tag punched
- Card Surface: Matte/ gloss finish
Pre-Designed Security Graphics
These can be pre-printed on cards for purchases off-shelf, or they can be combined with other artwork.
CardLogix Holofoil Cards
CardLogix Holofoil Cards are a cost-effective and non-peelable alternative to holographic laminates for increasing a card’s physical security. The holofoils are embedded within the card substrate, providing a smooth surface with no damage to print heads. CardLogix Holofoil Cards can be purchased off-the-shelf with several designs to choose from, or they can be built to order with your custom designs.
CardLogix ReadyStart™ Secure Cards
ReadyStart Secure Cards are a family of pre-printed ultra-high resolution 2400 dpi security background plastic cards that enable a rapid start in the physical security, personalization and issuance of smart card and eID Credentials. ReadyStart Secure Cards are available off-the-shelf in many popular and industry-specific ID card designs. They significantly reduce the time and expense of custom graphic designing and card printing. Corresponding ReadyStart background templates can be found in CardLogix Card Encoding Engine™ Card Personalization software.
Card Substrate Options
CardLogix’ standard card is constructed with white, commercial grade PVC substrate and a mirror-mirror finish for use with desktop printers. Other, higher-end card substrates are available.
Commercial Grade Cards
Commercial Grade Cards are general purpose card bodies for applications such as loyalty and libraries. The majority of PVC cards in your wallet today are made with Commercial Grade substrates, and they are the most cost effective option.
PVC (Polyvinyl chloride)
PVC is the most widely used material for plastic cards, and has been used for photo IDs for more than 10 years. Low in cost, the smooth surface of photo quality PVC material accepts dyes for high quality ID image printing and is compatible with most laminate materials.
PET (Polyethylene terephthalate)
PET is a polyester material that was used for many years for the punch laminate style of IDs. It is a crystalline plastic and has higher heat resistance than PVC. Durable and resistant to moisture and chemical attack, the material is typically used as an outer laminate for PVC, composite and Teslin cards. PET is more expensive than PVC, and is generally used as part of a multi-part card construction.
Biodegradable Grade Cards
These eco-friendly, biodegradable cards are manufactured from corn and based on the (NatureWorks® PLA) material. They look and feel identical to traditional plastic PVC cards.
Precision Identity Grade Cards
Precision Identity Grade Cards should be used when dimensional tolerances are critical and when the cards will be printed with additional graphic imaging (such as an employee badge).
Government Certified Cards
Government Certified Cards are uniquely built to meet ongoing card body certifications and requirements for different governments. CardLogix can help you come through with the toughest cards certified today.
Molded ABS SIM Cards
Molded ABS SIM Cards are designed for the specific demands of the Telecommunication industry. These cards have a higher Vicat softening point, and are best suited for the high temperatures in mobile devices and are rarely handled by the consumer.
PC (Polycarbonate)
Polycarbonate is an extremely durable thermoplastic polymer resistant to high temperatures and impact. Used in items like DVDs and CDs, it is receptive to offset security printing. PC is not compatible with variable printing, such as resin transfer or dye diffusion. When constructed with a very thin transparent laser receptive layer, PC cards can be laser engraved with very high definition graphics. Cards can be assembled with RFID, IC and contactless technology. PC is more difficult to manufacture, and is more expensive to produce than PVC or composite cards. PC cards are primarily used with laser technology to produce black images/text. PC or PC composite cards are typically used for the longest life and/or highest security IDs.
Manufacturer
Corporate Profile
CardLogix is an ISO 9001:2016-certified smart card manufacturer, software developer, and the premier provider of smart card technology with a comprehensive line of SDKs and tools that enable easy and rapid development of high quality smart cards. Since 1998, CardLogix has supplied millions of cards and card components to over 42 countries around the world. As an expert in smart card and chip technology, card operating systems, card software, development tools, and middleware, CardLogix has continuously been at the forefront of smart card technology.
CardLogix’ Mission
CardLogix’ mission is to make highly secure, high quality smart card systems more widely available to customers in need. CardLogix strives to make data transactions more secure, personnel and assets more protected, and to turn otherwise complex and expensive smart card systems into simpler, more cost-effective, and easier-to-develop solutions for everyone.
CardLogix Values
Trust is the primary commodity that CardLogix trades in every day. CardLogix builds and maintains customers’ confidence their products and processes, so that they can trust our cards to reliably protect personnel, sensitive data, and their most valuable assets. Starting with development software that’s flexible and easy to use to uncompromising customer support, CardLogix delivers on the promise of trust that our service inspires and our cards guarantee. Our company culture breeds initiative, commitment, and follow-through. As a global supplier and active industry participant, CardLogix understands the importance of being a responsible global business. With recycling, energy conservation, and full RoHS compliance, the company meets its goals with the environment in mind.
CardLogix Advantage
- Experts in smart card technology with an understanding of what it takes to get a card project from A to Z
- Commitment to ISO, ICAO, and industry conformance to ensure performance and interoperability
- Extensive partnerships with companies that offer complementary smart card infrastructure components
- Innovative products and solutions that simplify smart card development
- Cutting edge technology, sophistication and differentiated quality at a fraction of competitors’ costs
- Continuous customer support and involvement with evolving card projects
CardLogix Solutions
CardLogix manufactures high security and multi-functional ISO compliant smart cards, powered by CardLogix’ own operating systems. CardLogix offers easy-to-use SDKs for programmers, powerful middleware and APIs, a variety of applications software, and innovative solutions that empower end-users to develop and personalize smart cards without requiring any user-programming. The company partners with key suppliers in software, biometric capture, readers, and printers to deliver complete, leading-edge solutions. CardLogix smart card platforms provide solutions for multiple applications to markets globally, such as national, civil, voter and enterprise identity; physical and logical access cards; stored value; loyalty and rewards programs; e-purse; gaming, healthcare and other solutions that use a combination of multiple applications onto one card.
View CardLogix case studies.